
Gorgie
Gorgie ( GOR-gee) is a densely populated area of Edinburgh, Scotland. It is located to the west of the city centre, and borders Murrayfield, Ardmillan and Dalry.
1. Name
The name is thought to be Brythonic in origin. Early forms suggest it derives from gor gyn – upper wedge – which may refer to the tapering shape of the land between the Water of Leith and the Craiglockhart hills. An alternative derivation is 'big field' from Cumbric (Brythonic) gor cyn.
1. History
Gorgie is recorded in 12th century charters of Holyrood Abbey, when in 1236 it came into the possession of Sir William Livingston. In 1799, the Cox family who owned a mill bought most of the former estate from the residual Livingston family. They developed a glue factory on the site, which was redeveloped under a new Post Office Telecommunications telephone exchange in 1969. From 1527, the landowners lived in Gorgie House, situated on Alexander Drive. Its remnants were demolished in 1937, to allow construction of the Pooles Roxy cinema and some housing. Gorgie developed at a slower pace than nearby Dalry, allowing the continued operation of the 10 acres (4.0 ha) Gorgie pig farm until 1885. Robb's Loan is named after Robert Robb and his son James who farmed at Gorgie Mains for much of the nineteenth century. By 1800, only the area between Robertson Avenue and Saughton Park had any housing, served by a school and a church mission.
1. = Industry =
With grain whisky consumption growing in the industrialised and railway connected Victorian era, independent whisky blenders needed access to a high quality and high volume producer of grain whisky spirit. In 1885, major shareholders Andrew Usher, William Sanderson and John M. Crabbie, with numerous other whisky-blenders as shareholders, established the North British Distillery Company, which bought the former pig farm, and began developing a distillery. The distillery gained access to the Edinburgh Suburban and Southside Junction Railway, which began developing a railway station in Gorgie. This brought about the 1888 development of Stewart Terrace, Wardlaw Place, Wardlaw Street, . The tenement flats of Tynecastle Terrace that go halfway to mcleod street built 1898 ( date stone above the bathroom window at the top of the close next door) one of the last rows of tenements to be built in Gorgie it's joined onto the oldest row of tenements halfway along the block at Newton St on Gorgie Rd for which there is a date stone '1886' if one were to look up. There’s more date stones on three buildings at the junction of Wheatfield St, Gorgie Rd and Wardlaw Place. The south side of Gorgie Road 1887-1899 and north side 1896-1899 west of Newton Street. although Gorgie, west of Robertson Avenue, did not lose its rural character until the early 1900s.
McVitie & Price Ltd was established in 1830 on Rose Street in Edinburgh. The firm moved to various sites in the city, before completing the St. Andrews Biscuit Works factory on Robertson Avenue in 1888. Though the factory burned down in 1894, it was rebuilt the same year. It is one of the claimed sites of where the digestive biscuit was invented. The site was closed in 1969, when production ceased and operations were transferred to Levenshulme in Manchester, and Harlesden in London. After closure, Ferranti occupied the buildings as an electronics factory until the 1980s. In 1906, pharmaceutical research company T&H Smith Ltd moved from Canongate to the district. Now merged with two other Edinburgh-based medical research companies, they form medicinal-opiate producer MacFarlan Smith. The chemical plant of Cox's glue and gelatin works, and the Caledonian Brewery also developed in the area.
1. = Places of worship =
What is now Gorgie-Dalry Parish Church can be traced back to the Tynecastle church opened in 1891 after several years of outreach by Rev. George Wilson since 1885; it is affiliated to the Church of Scotland. St. Martin of Tours church is in the Anglican Communion Gorgie Gospel Hall belongs to the Open Brethren Christian tradition. In 1908 what is now Gorgie Mission Church was opened. Since 2008, Destiny Church, Edinburgh has been meeting in the converted former Bingo Hall.
1. Present
Most of the large industrial works closed from the late-1960s to the mid-1980s, bringing high unemployment to the area. The recent refurbishment of many of the older buildings has brought a more cosmopolitan nature to the district, allowing it to retain several smaller businesses. The area is served by Tynecastle High School. Gorgie City Farm was established by local people in 1982 on the site of a derelict railway goods yard. Set up as a community project with the aim of improving education in agriculture, horticulture and rural crafts for people living in the area. The farm closed in 2023, with community-led plans to re-open at a future point. In 2012, Gorgie was the centre of a Legionnaires' disease outbreak believed to originate from factory cooling towers in the area.
1. Representation
The Gorgie area is within the Edinburgh South West constituency for the Westminster Parliament and, since 2024, is represented by the Rt Hon Scott Arthur MP of the Labour Party. At the Scottish Parliament, the area falls within Edinburgh Central, currently represented by Angus Robertson MSP of the Scottish National Party. The area, as part of the Sighthill/Gorgie ward, elects four councillors to the City of Edinburgh Council. The current representation is: Denis Dixon and Catherine Fullerton (both SNP), Donald Wilson (Scottish Labour Party) and Ashley Graczyk (Conservatives).
1. Demographics
1. Transport
The area was traversed by both the Caledonian Railway and the North British Railway and was served by Gorgie East Station (named Gorgie Station until 1952) on the Edinburgh Suburban and Southside Junction Railway. It was opened on 1 December 1884 and served the area until it was closed in 1962 when passenger rail services were withdrawn from the Edinburgh Suburban line as part of the British Railways rationalisation programme known as the Beeching Axe. No trace of the station remains but the route continues to be used for freight services to this day, so freight trains avoid Edinburgh's main stations of Edinburgh Waverley and Edinburgh Haymarket, and occasionally diverted passenger trains also pass along this line.
1. = Future =
A local campaigning group, the Capital Rail Action Group (CRAG), ran a campaign for the ESSJR line to be re-opened to passenger services, and proposed that it should be operated either as a commuter rail service or as a light rail system to form an extension of the forthcoming Edinburgh Tram Network. Following a petition submitted to the Scottish Parliament in 2007, the proposal was rejected in 2009 by transport planners due to anticipated cost.
1. Heart of Midlothian F.C.
After Heart of Midlothian F.C. was formed in 1874, the club played at sites in the Meadows, Powburn and Powderhall. Hearts first moved to Gorgie in 1881. This pitch stood on the site of the present-day Wardlaw Street and Wardlaw Terrace. As this site was then regarded as being "out of town", Hearts would sometimes stage two matches for the price of one, or set an admission price much lower than Edinburgh derby rivals Hibernian. In 1886, with the city continuing to expand, tenements replaced the old ground and Hearts moved across Gorgie Road to the present site, which was leased from Edinburgh Corporation. They still play today at Tynecastle Park in the Scottish Premiership.
1. Notable residents
James Lind (naturalist)
1. See also
Gorgie-Dalry
1. References
1. Sources
Inglis, Simon (1996). Football Grounds of Britain. Collins Willow. ISBN 0-00-218426-5.
1. External links
Bartholomew's Chronological map of Edinburgh (1919)
Gorgie-Dalry Community Council
Nearby Places View Menu
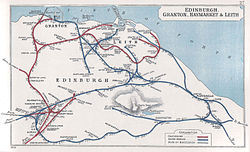
Gorgie East railway station
Shandon, Edinburgh

Merchiston railway station


 English
English
 Français
Français